The Gallup survey revealed that 62% of Americans drink alcohol frequently. A recent study published by the American Heart Association described alcohol as the leading cause of death in 65% of heart failure cases. Alcohol and its effects are innumerable to imagine, and people often get confused and ask: Is alcohol a stimulant or some other type of chemical altering brain and bodily functions? We have explained everything from alcohol, its kind, its effects, and the way of getting rid of it!
Embrace the journey free of alcoholism with ChoicePoint alcohol rehab, get in touch to seek immediate help from any side effects, or book appointments 844.445.2563.
Table of Contents
Stimulants Vs. Depressant: Know the Difference First!
Any substance affecting brain activity could either be a stimulant or a depressant. Some of the significant differences could be:
Stimulants |
Depressants |
| Make people more alert after taking substances. | Makes people more inactive, relaxed, and tired after substance use. |
| Stimulates the central nervous system. | Depresses or down-regulates the nervous system. |
| Releases the neurotransmitter dopamine and norepinephrine that are involved in producing euphoria, | Stimulates the release of GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) that inhibits brain activity, causing drowsiness. |
| The use is associated with increased heart rate and blood pressure. | Usually, it lowers the heart rate and blood pressure. |
Examples of common stimulants include:
|
Examples of common depressants include:
|

Did you know? The misuse of alcohol among adolescents can alter brain development, producing long-term changes in brain structure and function.

Did you know? The misuse of alcohol among adolescents can alter brain development, producing long-term changes in brain structure and function.
Is Alcohol A Stimulant: Understand its Effects
Now, the answer to the main question is: Is alcohol a stimulant? Many people believe that alcohol is a stimulant because of the initial surge of energy associated with its use. But despite some stimulating effects, alcohol is classified as a depressant.
Effects of Alcohol on the Body and Brain
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse And Alcoholism (NIAAA) states that alcohol interferes with the communication pathways between the brain and the body.
It enhances the effects of GABA and glutamate, resulting in a dull state of mind. Excess drinking can suppress the central nervous system to such an extent that it can produce symptoms such as
- Slurred speech
- Decreased motor coordination
- Uncoordinated movements
- Blackouts
- Distorted judgment
- Reduced ability to think straight
- Respiratory failure (in extreme cases)
- Coma or death (in extreme cases)
Side Effects of Alcoholism
There is no denying that a drink after a hectic day can be relaxing. However, WHO (World Health Organization) has stated intense research that “no level of alcohol consumption is safe for our health; risk starts from the first drop.”
Does it seem a bit intense? Let’s investigate the scientific evidence to find out why this statement holds.
Alcoholism And Risk Of Cancer
The National Cancer Institute lists alcohol as a known carcinogen. Alcohol can cause 7 types of cancer, including head and neck cancer, breast cancer, and liver cancer.
When you consume alcohol, it is metabolized by the body. One of the metabolites, acetaldehyde, can damage the DNA. DNA controls the normal growth of the cell. When it gets damaged, the cells divide uncontrollably, leading to cancer.
Alcoholism Has Been Linked To Liver Damage
Prolonged alcohol use has been linked to alcohol-related liver diseases. Alcohol is metabolized in the liver. Excessive use causes the buildup of lipids and fats, resulting in fatty liver. Furthermore, alcoholism has also been linked to liver cirrhosis (permanent liver damage).
Other side effects include:
- High blood pressure
- Heart diseases
- Digestive issues
- Learning and memory issues
- Dementia

Did you know? That in the U.S., end-stage liver diseases among people aged 25-35 years rose more than 10% annually? One major cause was alcohol-related liver diseases.

Did you know? That in the U.S., end-stage liver diseases among people aged 25-35 years rose more than 10% annually? One major cause was alcohol-related liver diseases.
Overcome the Depressing Effects: Recovery from Alcoholism
Addiction is a terrible disease that sneaks up on you without you even realizing it. The good news is that it is treatable. But, to quit drinking, you must first accept and understand your drinking problem. From there, you can redirect your mind towards recovery goals.
A. Managing Mental Health Issues Leading To Alcoholism
The key to a successful recovery lies in identifying the cause of addiction. A majority of people start drinking as a coping mechanism to avoid dealing with troubling mental health issues. For example, people experiencing anxiety may start drinking to calm their nerves. But, using alcohol as a coping mechanism can lead to lifelong dangerous consequences. So, talking to a mental health professional to better manage your emotions and alcohol issues is essential.
B. Combat Alcohol Cravings and Withdrawal with Medicated Detox
Have you tried to give up drinking before, but after 2 or 3 days, you relapsed because of intense cravings and withdrawal symptoms? You can completely abstain from alcohol through a medical detox. A medical detox uses FDA-approved medications combined with psychotherapy and counseling for a wholesome recovery. It can ease withdrawal symptoms such as
- Vomiting and nausea
- Intense cravings
- Headache
- Agitation (state of anxiety and nervousness)
- Tremors
Alcohol addiction treatment is different for everyone. Some commonly prescribed medications may include:
- Naltrexone – reduces cravings and relapse rates
- Acamprosate – is used in the maintenance phase of the treatment. Helps to reduce cravings and ease withdrawal symptoms –
- Disulfiram- helps abstain from alcohol by creating unpleasant symptoms if you consume alcohol
Many people are unaware of the dangerous interactions of alcohol with medications, including Diflucan, Xanax, Suboxone and Tramadol. Taking alcohol with these medications slows down recovery and may worsen your liver health. Get help from DEA-certified addiction specialists and start your recovery journey today!
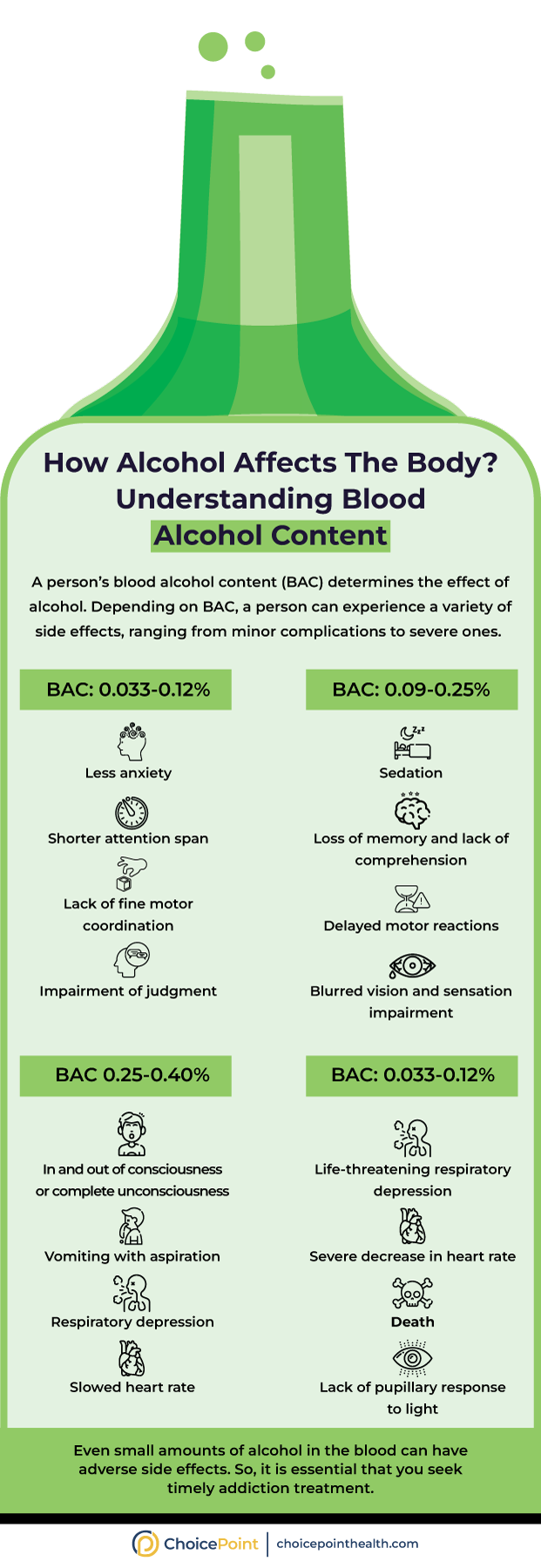
Alcohol’s Effects on the Body
A Deep Dive into Psychological Recovery Through Psychotherapy
Mental health illness and alcoholism are often interlinked. Alcohol affects the working of our brains. It affects the fine balance between neurotransmitters that play an important role in maintaining emotions and overall mental health.
To fully recover from addiction, it is essential to treat underlying mental health conditions. Psychotherapy is a great way to regulate your emotions for improved quality of life. Some therapies that can help with substance use disorders include:
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
- Group Therapy
- Individual Therapy
- Dual Diagnosis
You can now recover in your house through virtual therapy sessions. To book your first consultation for holistic healing, please call us at 844.445.2563.
Reviving a Depressed Personality with Counseling
Addiction treatment is like having a second chance at life. Through holistic care, you gain a fresh new perspective on life. You work towards regaining what you have lost. Addiction counselors work with you to guide you through the recovery process. They provide positive insights on sustainable recovery and relapse prevention. They bridge the gap between you and the available resources for treatment and maintaining sobriety.
Take the first step towards an addiction-free life. Call 844.445.2563, a confidential helpline, for personalized support and guidance on your journey towards recovery.
Final Verdict: Break Free From Alcohol Inconsistency With ChoicePoint
We started by answering your question, Is alcohol a stimulant? Alcohol is a depressant, and alcohol abuse can have deadly consequences. The mechanism of action of alcohol might seem unimportant now that you know the deadly consequences and side effects of alcohol abuse.
If you or a loved one is suffering from addiction, please call us at 844.445.2563. Our uniquely tailored plans comply with all confidential and ethical guidelines. We go the extra mile to provide excellent customer service and top-quality treatment to make recovery more accessible.

Did you know? People with ADHD are more likely to get entangled in the cycle of alcohol binge drinking as they are more prone to its effects as a stimulant!

Did you know? People with ADHD are more likely to get entangled in the cycle of alcohol binge drinking as they are more prone to its effects as a stimulant!
Further Queries Answered Regarding Is Alcohol a Stimulant?
Learn more about alcohol and its effects;
How Long Does It Take Alcohol to Leave Your System?
The rate at which the body metabolizes alcohol depends on how much alcohol you consume, genetics, and age. Alcohol stays in the system for 6-72 hours. It can be detected in
- Blood – up to 12 hours
- Breath 12-24 hours
- Urine 12-24, 72 hours in case of binge drinking
- Saliva – up to 12 hours
- Hair- up to 90 days
What Is a Social Drinker?
A social drinker is a person who drinks occasionally in moderate quantities at social gatherings.
Can You Drink Alcohol While Taking Antibiotics?
Alcohol in moderate quantities does not reduce the effectiveness of antibiotics. However, it is recommended to avoid alcohol because of these side side-effects:
- Dehydration
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Liver damage
How Much Alcohol Is in Beer?
The alcohol content in beer is indicated by ABV (Alcohol By Volume). The beer’s alcohol content is as follows:
- Light beer: 4-5%
- Regular bear: 5-6%
- Craft beer: 6-10%
- Stronger beers can go up to 15% alcohol or more
What Is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
Fetal alcohol syndrome is a condition that occurs in a newborn exposed to alcohol before birth during the pregnancy. The Signs and symptoms may include:
- Small eyes
- Exceptionally thin upper lips
- Smooth skin between nose and lips
- Small head circumference
Medical Disclaimer:
ChoicePoint aims to improve the quality of life for people struggling with substance use disorder and mental health issues. Our team of licensed medical professionals research, edit and review the content before publishing. However, this information is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. For medical advice please consult your physicians or ChoicePoint's qualified staff.











Review Is Alcohol a Stimulant? Knowing the Effects and Treatment.